
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Hunan Key Laboratory of Nanophotonics and Devices, School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
2 Key Laboratory of Hunan Province for Statistical Learning and Intelligent Computation, School of Mathematics and Statistics, Hunan University of Technology and Business, Changsha 410205, China
Two-dimensional (2D) nonlinear optical mediums with high and tunable light modulation capability can significantly stimulate the development of ultrathin, compact, and integrated optoelectronics devices and photonic elements. 2D carbides and nitrides of transition metals (MXenes) are a new class of 2D materials with excellent intrinsic and strong light-matter interaction characteristics. However, the current understanding of their photo-physical properties and strategies for improving optical performance is insufficient. To address this issue, we rationally designed and in situ synthesized a 2D Nb2C/MoS2 heterostructure that outperforms pristine Nb2C in both linear and nonlinear optical performance. Excellent agreement between experimental and theoretical results demonstrated that the Nb2C/MoS2 inherited the preponderance of Nb2C and MoS2 in absorption at different wavelengths, resulting in the broadband enhanced optical absorption characteristics. In addition to linear optical modulation, we also achieved stronger near infrared nonlinear optical modulation, with a nonlinear absorption coefficient of Nb2C/MoS2 being more than two times that of the pristine Nb2C. These results were supported by the band alinement model which was determined by the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) experiment and first-principal theory calculation. The presented facile synthesis approach and robust light modulation strategy pave the way for broadband optoelectronic devices and optical modulators.
MXenes optical properties modulation in situ growth carriers transfer nonlinear optical absorption Opto-Electronic Advances
2023, 6(10): 220162

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Hunan Key Laboratory of Nanophotonics and Devices, School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
A new unsaturated wind-chime model is proposed for calculating the formation time of the diffraction rings induced by spatial self-phase modulation (SSPM) in molybdenum disulfide suspension. To optimize the traditional wind-chime model, the concentration variable of 2D materials was introduced. The results of the unsaturated wind-chime model match quite well with the SSPM experimental results of molybdenum disulfide. Based on this model, the shortest formation time of diffraction rings and their corresponding concentration and light intensity can be predicted using limited data. Theoretically, by increasing the viscosity coefficient of the solution, the response time of the diffraction ring, to reach the maximum value, can be significantly reduced. It has advanced significance in shortening the response time of photonic diodes.
spatial self-phase modulation wind-chime model nonlinear optics Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(1): 011901
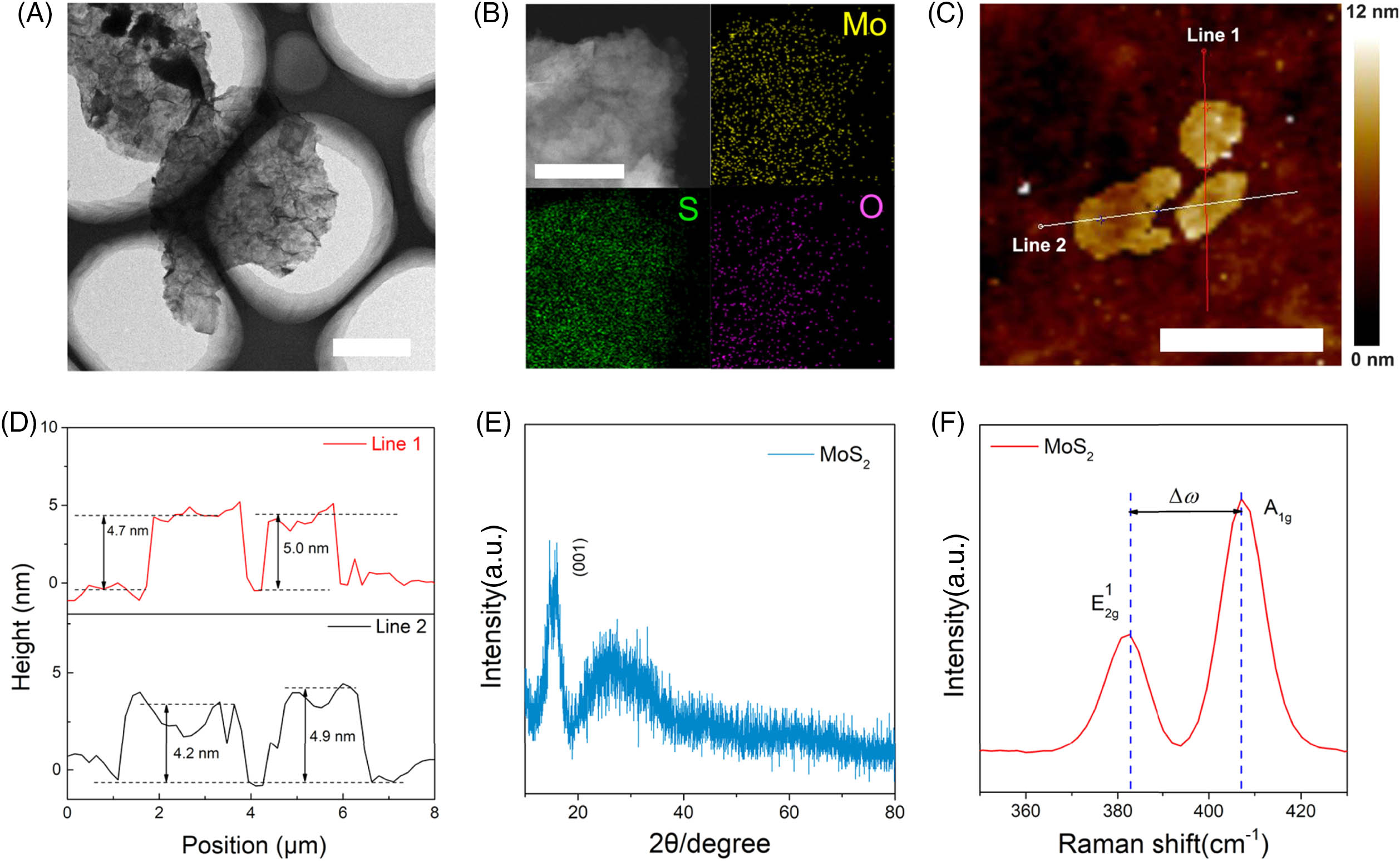
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Hunan Key Laboratory for Super-microstructure and Ultrafast Process, School of Physics and Electronics, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
2 e-mail: junhe@csu.edu.cn
3 e-mail: wyw1988@csu.edu.cn
The reorientation of 2D materials caused by nonlocal electron coherence is the formation mechanism of 2D material spatial self-phase modulation under laser irradiation, which is widely known as the “wind-chime” model. Here, we present a method that provides strong evidence for the reorientation of 2D-material-induced spatial self-phase modulation. The traditional “wind-chime” model was modified by taking into account the attenuation, i.e., damping of the incident light beam in the direction of the optical path. Accordingly, we can extract the nonlinear refractive index of a single nanosheet, instead of simply obtaining the index from an equivalent film that was constructed by all nanosheets. Our approach introduces a universal and accurate method to extract intrinsic nonlinear optical parameters from 2D material systems.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(11): 11001725
1 北京理工大学光电学院, 北京 100081
2 北京理工大学深圳研究院, 广东 深圳 518057
提出一种面向数字全息的相位畸变自动补偿方法,利用图像分割技术对被检测物体进行自动分割,生成相位掩模板,进而得到不含被测物体区域的畸变相位。基于相位畸变校正模型对畸变相位进行最小二乘拟合,最终实现相位畸变的自动补偿。实验中搭建了数字全息检测平台,并对晶圆表面进行测量,结果表明所提出的方法能够实现畸变相位的自动校正。
全息 畸变校正 图像分割 三维测量 光学学报
2018, 38(12): 1209001
1 中南大学物理与电子学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
2 国防科学技术大学理学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
采用多孔氧化铝(AAO)模板作为基底,结合真空蒸镀、热去湿技术实现金纳米颗粒的有序组装。通过二次氧化技术制得孔径80 nm、壁厚20 nm左右的多孔氧化铝模板,在模板表面真空蒸镀一层很薄的金膜,随后将样品放入管式炉中做退火处理。在扫描电子显微镜下对其形貌进行表征,发现多孔氧化铝模板表面金纳米颗粒具有很好的有序度;同时对于具有较浅孔的模板,有序孔阵列组装得到的金纳米颗粒阵列呈现高度有序性,且与孔阵列密排六方结构相匹配。采用紫外可见光分光光度计在300~800 nm波长范围内对表面成功组装金纳米颗粒阵列的样品吸收特性进行了测量,结果表明多孔氧化铝模板组装金纳米颗粒阵列后吸收谱图出现明显的表面等离子体吸收峰,峰位置在316 nm和616 nm处,较普通金纳米颗粒吸收峰位置出现大幅度的红移。
材料 金纳米颗粒阵列 自组装 多孔氧化铝模板 表面等离子体 光学学报
2013, 33(s2): s216002





